Yuu Jinnai
Home
Google Scholar
GitHub
Current Research:
Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding
Language Model Alignment
Prior Projects:
Parallel Best-First Search
Automated Skill Discovery
日本語:
Japanese
Open Data Structures
ヒューリスティック探索入門
Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by orderedlist
Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding for Text Generation
Minimum Bayes Risk (MBR) decoding is a decision-theoretic approach to text generation that selects outputs by minimizing expected risk under a utility metric, rather than simply choosing the most probable sequence. While it generates significantly improved text under several tasks, MBR decoding faces challenges in computational efficiency, hyperparameter selection, and scalability.
My research develops efficient and effective MBR decoding methods that address these challenges through model-based approximations, adaptive algorithms, optimal transport theory, and theoretical analysis.
Overview
MBR decoding generates text by:
- Sampling a set of candidate outputs from a language model
- Computing expected utility between candidates using a metric (e.g., BLEU, COMET)
- Selecting the candidate that maximizes expected utility
Despite its promise, classical MBR is computationally expensive and requires careful tuning. Our work makes MBR practical for real-world applications.
Contributions
Model-Based MBR Decoding
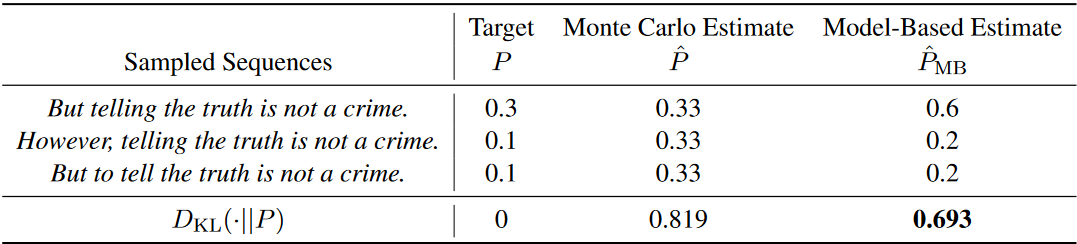
Problem: Classical MBR requires computing pairwise metrics between all sampled candidates (O(n²) comparisons), making it prohibitively expensive for large sample sizes.
Solution: We developed model-based MBR, which trains a lightweight neural model to directly predict expected utility scores, reducing computational cost while maintaining or improving quality.
Publication: Jinnai Y, Morimura T, Honda U, Ariu K, Abe K. 2024. Model-based Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding. Proc. 41st International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-24).
PAPER | CODE | TALK
Hyperparameter-Free MBR
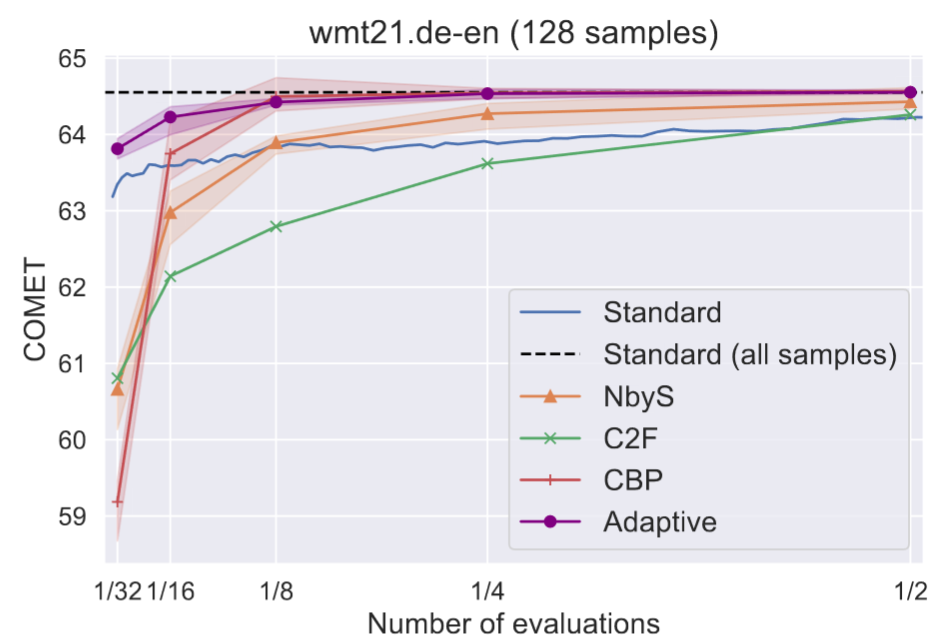
Problem: MBR decoding requires selecting the number of samples, which significantly impacts both quality and computational cost. Poor choices lead to suboptimal results.
Solution: We proposed an adaptive algorithm that automatically determines the optimal sample size during decoding, eliminating manual hyperparameter tuning while improving efficiency.
Publication: Jinnai Y, Ariu K. 2024. Hyperparameter-Free Approach for Faster Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL-24 Findings).
PAPER | CODE | TALK
Diverse and High-Quality Text Generation
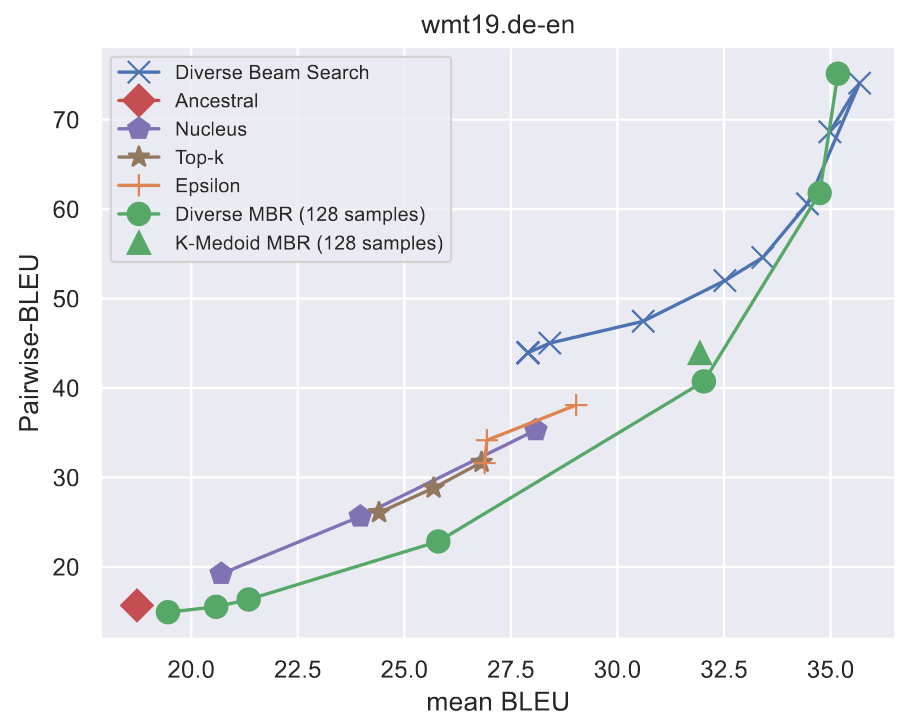
Problem: Standard MBR tends to select consensus outputs, lacking diversity. Many applications require generating multiple diverse, high-quality options.
Solution: We extended MBR to generate diverse outputs by sequentially selecting candidates that maximize utility while maintaining diversity, enabling applications like creative writing and summarization.
Publication: Jinnai Y, Honda U, Morimura T, Zhang P. 2024. Generating Diverse and High-Quality Texts by Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL-24 Findings).
PAPER | CODE | TALK
Document-Level MBR with Optimal Transport
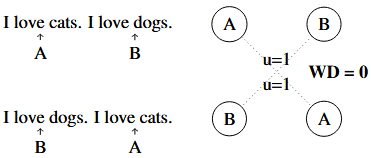
Problem: Existing MBR methods use sentence-level metrics like COMET, which fail to capture document-level coherence and structure in long-form generation tasks.
Solution: We developed a document-level MBR approach using optimal transport to measure semantic alignment across entire documents, improving coherence in multi-sentence generation.
Publication: Jinnai Y. 2025. Document-Level Text Generation with Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding using Optimal Transport. Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL-25).
PAPER | CODE | TALK
Theoretical Guarantees for MBR
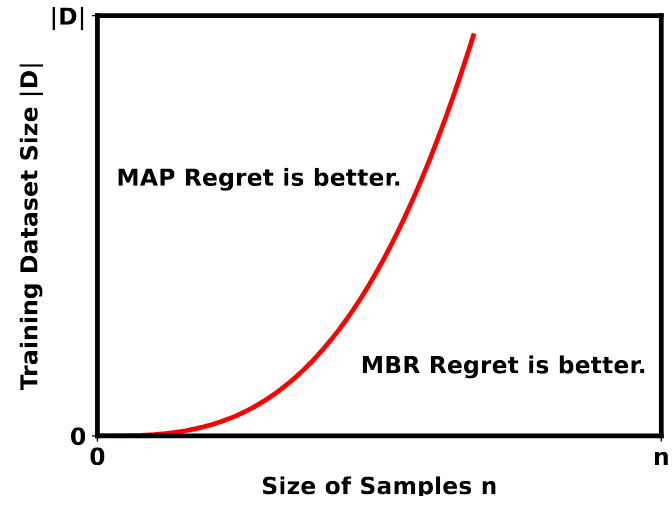
Problem: While MBR is widely used, theoretical understanding of when and why it works has been limited.
Solution: We provided theoretical guarantees for MBR decoding, establishing conditions under which MBR provably improves over alternative decoding methods.
Publication: Ichihara Y, Jinnai Y, Ariu K, Morimura T, Uchibe E. 2025. Theoretical Guarantees for Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding. Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL-25).
PAPER
Understanding MBR’s Distribution Approximation

Problem: MBR uses Monte Carlo sampling to approximate the true distribution, but how sample size affects this approximation was not well understood.
Solution: We analyzed the relationship between sample size and distribution approximation quality, providing guidance on sample size selection and identifying when MBR exhibits anomalous behavior.
Publication: Ohashi A, Honda U, Morimura T, Jinnai Y. 2024. On the True Distribution Approximation of Minimum Bayes-Risk Decoding. In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL-24).
PAPER | CODE | TALK
Talks and Tutorials
- Jun. 2025: Introduction to Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding. NLP Colloquium. SLIDES
All MBR Publications
- Jinnai Y. 2025. Document-Level Text Generation with Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding using Optimal Transport. ACL-25.
- Ichihara Y, Jinnai Y, Ariu K, Morimura T, Uchibe E. 2025. Theoretical Guarantees for Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding. ACL-25.
- Jinnai Y, Morimura T, Honda U, Ariu K, Abe K. 2024. Model-based Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding. ICML-24.
- Jinnai Y, Ariu K. 2024. Hyperparameter-Free Approach for Faster Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding. ACL-24 Findings.
- Jinnai Y, Honda U, Morimura T, Zhang P. 2024. Generating Diverse and High-Quality Texts by Minimum Bayes Risk Decoding. ACL-24 Findings.
- Ohashi A, Honda U, Morimura T, Jinnai Y. 2024. On the True Distribution Approximation of Minimum Bayes-Risk Decoding. NAACL-24.
Software and Code
All code is publicly available on GitHub: